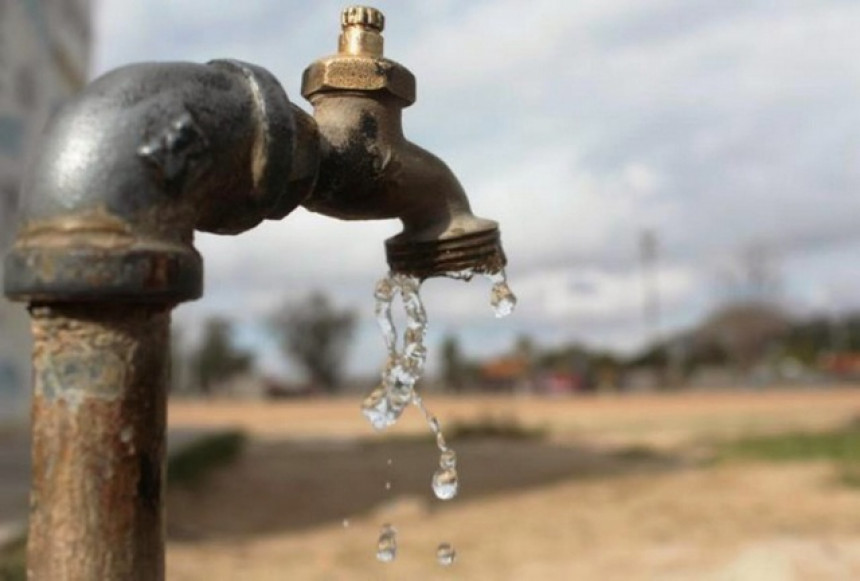
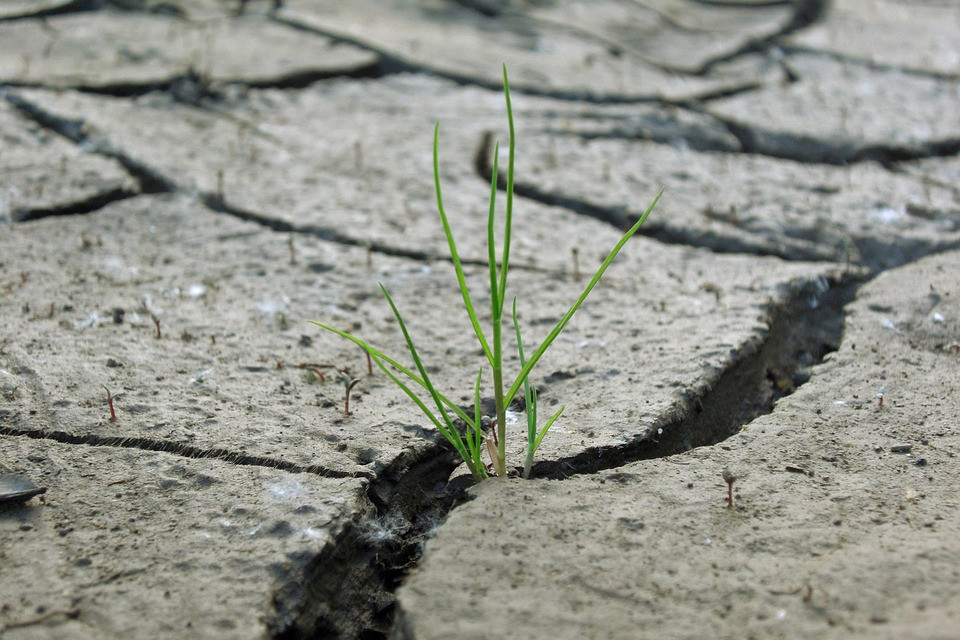
Droughts impose limitations on economic, social and environmental creation of a territory. Its effects are numerous and the water supply to townships, irrigation or industry may be restricted during a drought and aquatic ecosystems suffer the consequences of reduced flow in rivers. The duration and impacts of droughts vary by country. While in those lacking water storage and output infrastructure, water supply depends directly on rainfall, a decrease in rainfall for several months can lead to drought in other countries that have sufficient of water storage infrastructure, the greatest impacts occur when water shortages occur for several consecutive years.
The effects of drought can be aggravated in areas with limited resources and imbalances between them and water demands. In addition, experts and scientists from around the world predict that the greatest impacts of climate change on water resources will occur in the regions of the European Union (EU) more vulnerable to shortages and drought, as in the case of Spain.
Traditionally, most countries have considered drought as a crisis situation where urgent action must be applied. However, in recent years this approach has changed worldwide. In particular, in Spain and in other Member States of the European Union, it has gone from a crisis management approach to one of planned risk management. Also in the European Union several highly relevant policy instruments have been prepared including, among its objectives, combating the negative effects of drought. Examples of these instruments are the Water Framework Directive, the Communication "Addressing the challenge of water scarcity and droughts in the European Union", the "Plan for the protection of Europe's water resources" and the recent communication "A strategy Europe on adaptation to climate change."
Spain is a country of the European Union with a high variability in the temporal and spatial distribution of water resources, which results in many areas in its territory being affected by water shortages and frequent droughts. The implementation of policies and actions and the implementation of a system of indicators at national level, the creation of drought management plans at the river basin level and the involvement of users and civil society, are minimizing the socio-economic and environmental impacts of droughts. Most of these policies have their origin in the severe drought that occurred in Spain between 1991 and 1995. Its high economic, social and environmental impacts served to make the authorities deem drought as in fact being normal and recurring in a climate such as we in Spain, and that management policies drought stop adopting a crisis management approach and take on another of a planned drought risk management approach.